5G and all its benefits: a review
Vassilis Seferidis, CEO and Co-Founder of Zeetta Networks
Original source: https://www.mobile-magazine.com/5g-and-iot/zeetta-networks-5g-review
Noise around 5G grew louder and louder in 2020, catching the attention of consumers, businesses and specialist sectors alike. It wasn’t all talk either, tremendous progress has been made throughout the year when it comes to testing and developing the use-cases for 5G.
This progress will continue to gain momentum into 2021. In fact, many experts believe 5G will be one of the largest and fastest growing markets over the next five years. As the new year is fast approaching, it feels an appropriate moment to reflect on this year's learnings and consider what is to come.
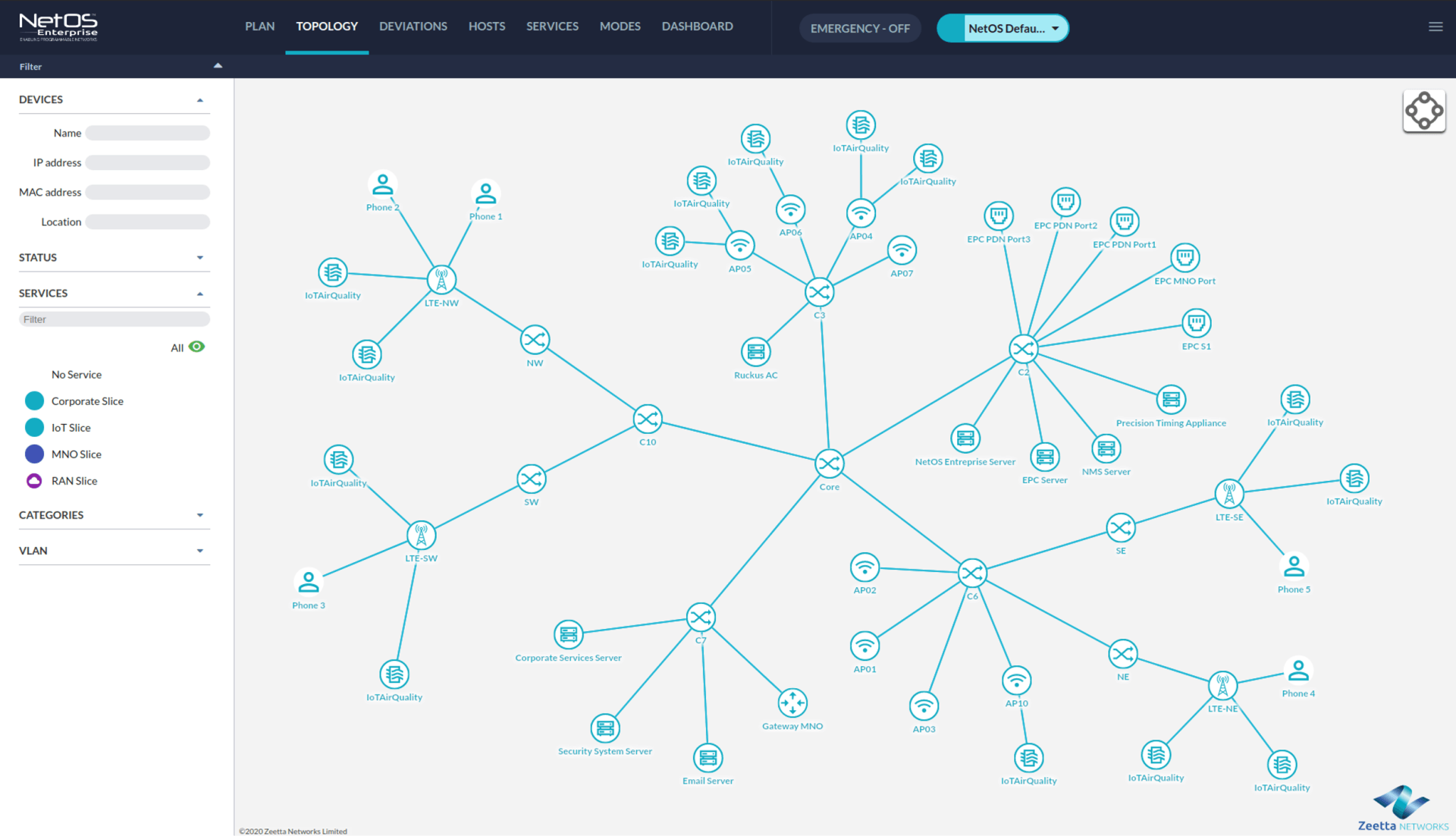
Private 5G networks
One particular aspect of 5G that has gained traction throughout 2020 is the building and testing of private 5G networks. Such a network uses cellular 5G technology to create a dynamically reconfigurable network to provide specific bandwidth and latency to a local area network. Utilising a private 5G network enables greater control and can be far more cost effective for a business. Looking at how these networks will be useful across sectors are projects such as 5G-ENCODE which are working to establish specific business use cases for 5G in advanced manufacturing.
In 2021, we’ll continue to see updates shared from these sorts of projects on the progress made in developing private 5G networks. Business use cases will become far more tangible for organisations across sectors within the UK. Indeed, 5G-ENCODE has already launched phase one of its private network, with phase two to follow in the first half of 2021.
Network slicing and splicing
Private 5G networks will need to interact with public and private networks, if the benefits are not to end at the enterprise boundary. In order to facilitate this, operators need to be able to join together bespoke user network slices across multiple domains. Network slicing and splicing is how that can be done. The application of this feature has been researched and developed throughout 2020, and supports a wide range of applications, enabling enterprises to create customised networks specifically tailored to their needs. Utilising network slicing and splicing ensures only the correct level of connectivity is shared to each machine, therefore optimising performance and creating cost savings.
In 2021, we’ll begin to see a far greater understanding from businesses on the specific benefits that network slicing and splicing can bring to their organisations. As a result, we’ll see an increase in demand for access to this technology.
UK investment
Looking back at 2020, it’s undeniable that the UK government has demonstrated its commitment to understanding and deploying 5G in a wide range of environments. An example of this is the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sports’ 5G Testbeds and Trials Programme, which aims to explore the benefits and challenges of deploying 5G across all of the UK’s sectors. The investment in testbeds across the country aims to ultimately boost the productivity and growth of UK industries. 5G-ENCODE is one such testbed.
5G-ENCODE has been set up to explore the application of 5G in industrial settings. Led by Zeetta Networks, the 5G-ENCODE project will see a 5G private network built at the National Composite Centre (NCC).
Looking ahead, the government has already confirmed its commitment for the year and the same level of support is set to continue. In 2021, the government is investing £50 million in 2021 as part of a £250 million commitment to building a secure and resilient 5G network.
Long term opportunity for telecommunications
Telecommunications organisations have long touted the benefits of 5G within a business and consumer context. However, many have concluded that for exponential return on investment they need to be positioned to deploy 5G networks in business settings. To explore this and establish their positions within the race, many operators have already engaged with projects such as O2 and 5G-ENCODE and Vodafone and Midlands Future Mobility.
In 2021, as business use cases start to become increasingly tangible, we’re likely to see these organisations elevate their efforts to establish leadership in this space. Additionally, business use cases could open up new markets for telecommunications operators to build stronger relationships with where they might not have previously.
Offsetting carbon emissions
Reducing business environmental impact has become imperative throughout 2020. Sustainable business models are crucial, particularly as public opinion and government legislations have changed. We’ve already seen many businesses take steps to reduce their carbon footprint through reducing emissions or offsetting programmes.
Moving forward, we’ll see more businesses look to 5G and the benefits it can offer in helping them to operate more efficiently and sustainably. 5G networks will enable organisations’ supply chains to work far more efficiently. Within a factory, for example, the level of automation that 5G will bring will enable organisations to run at lower costs, shorter lead times for factory floor production, and greater flexibility. In fact, research from O2 found that the introduction of 5G to manufacturing processes could take up to 40 Megatonnes of carbon out of the economy by 2035.
Disrupting business
We already know that deploying 5G technology will be transformational for organisations in almost every sector. As use cases continue to be discovered, businesses will be empowered to use 5G to reach bigger and better goals. One thing certain though is that 2021 will be the year we begin to see 5G disrupt business environments.